ホワイトペーパー
Interpreting TactileGlove Data for Practical Use Cases
This white paper provides guidance on understanding data collected by the PPS TactileGlove sensor, particularly in basic gripping and lifting tasks. It covers what to expect, how well the sensor performs, ways to reduce errors, and how to accurately interpret force and pressure readings.
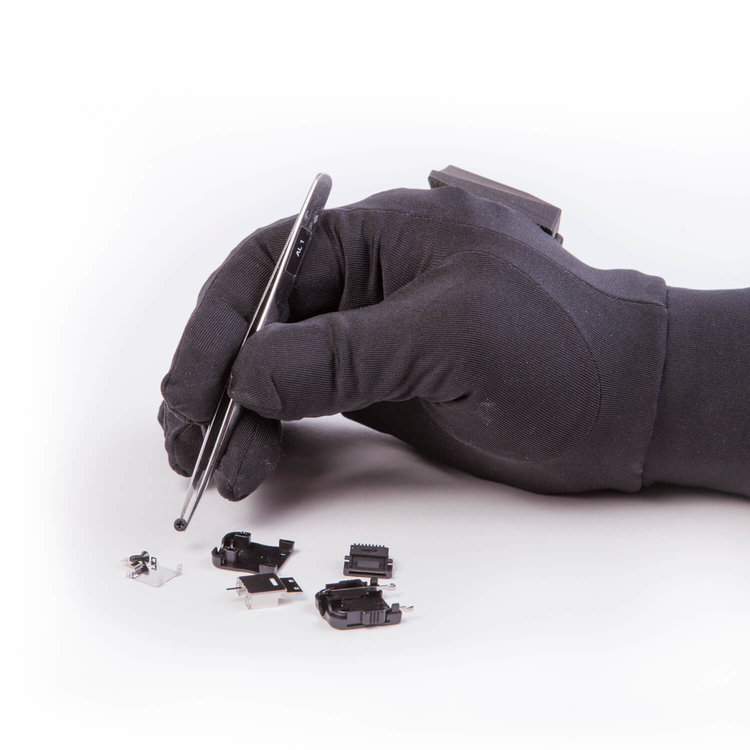
The PPS TactileGlove is an advanced tool for testing ergonomics, offering precise measurements of hand pressure during various activities. Its high-speed data capture, consistency, and comfortable design make it invaluable for assessing comfort, fit, and safety in product development.
Using quantified data from tactile interactions is becoming standard practice in ergonomic testing. This shift allows designers to move from relying solely on subjective feelings to having concrete measurements, facilitating better design decisions and reducing the need for multiple design revisions.
触覚手袋による手の人間工学の定量化
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) are injuries or disorders of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints and cartilage. Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSD) are conditions caused, prolonged or made worse by work conditions.
Ergonomics / human factors considers the interaction between humans and other parts of a system. A goal of ergonomics is to reduce stress and eliminate injuries and disorders associated with the overuse of muscles, bad posture, and repeated tasks. A workplace ergonomics program can aim to prevent or control injuries and illnesses by eliminating or reducing worker exposure to WMSD risk factors using engineering and administrative controls. Risk factors include awkward postures, repetition, material handling, force, mechanical compression and duration of exposure.
There is strong evidence that job tasks that require a combination of risk factors (e.g., highly repetitious, forceful hand/wrist exertions) increase risk for hand/wrist tendinitis. Fifty percent of industries reported work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSD) rely heavily on the use of hand tools.
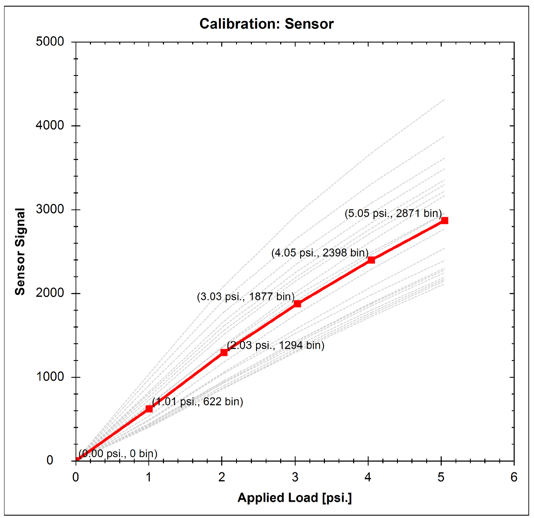
触覚圧力センサーのキャリブレーションと検証
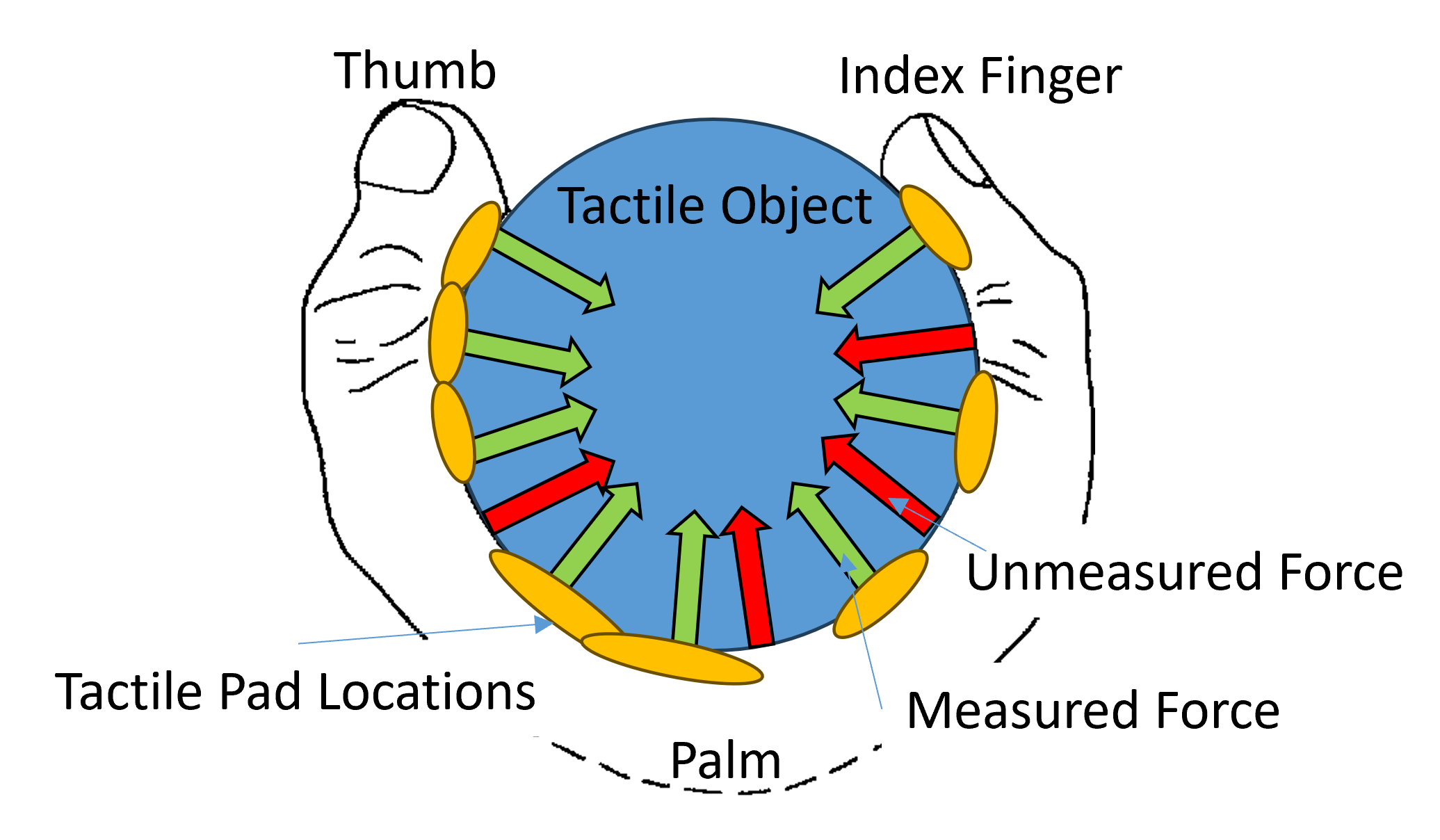
触覚センシング involves measuring the force and pressure distributions across an area between two surfaces in direct, physical contact. However, while the common measurand terms of force and pressure may be used, the mechanics of the application are often much more complex.
圧力はスカラー値であり、特定の領域に対する力として定義されます。力は、特定の大きさと方向を持つベクトルと見なすことができます。ロード セルなどの従来の 1 軸測定デバイスは、3 つの方向成分の 1 つまたは複数を分離して測定できる、適切に制御された 1 つの点に接触を集中させるために、精密なたわみを組み込むことができます。
ただし、薄くて柔軟な触覚圧力センサーを検討する場合、キャプチャしようとしているのは 2 つの表面間の相互作用であり、したがって、これらの複雑な測定は、全体に対するセンサー自体の影響と侵入を最小限に抑えながら、表面相互作用の境界で行う必要があります。応用。
これは、触覚センサーの性能を正確に設計、キャリブレーション、および検証することは困難な作業であり、慎重に検討する必要があることを意味します。このドキュメントは、キャリブレーションに影響を与えるパラメータと、プロセスおよび最終結果自体のパラメータの両方をよりよく理解するためのガイドとして役立つことを目的としています。